Power Generating facade
Compiled by: Ar. Vibhor Bhartiya
Renewable energy replaces conventional fuels in four distinct areas:power generation, hot water/space heating, transport fuels, and rural (off-grid) energy services
Mainstream forms of renewable energy :
- Wind Power
- Solar Energy
- Hydro Power
- Biomass
- Bio fuel
- Geothermal Energy
Need for Power Generation :
- Global demand for energy will more than double by mid-century and more than triple by the century’s end.
- Growing population and increase in power consumption.
- Solar radiation, along with secondary solar-powered resources such as wind and wave power, hydroelectricity, and biomass, account for most of the available renewable energy on earth.
- Isolation for building owners from future energy price increases.
- Increased comfort due to more-uniform interior temperatures.
- Reduced requirement for energy austerity.
- Reduced total cost of ownership due to improved energy efficiency
- Reduced total net monthly cost of living.

Nellis Solar Power Plant in the United States,the largest photovoltaic power plant in North America.



Building-Integrated Photovoltaic (BIPV)
Photovoltaic (PV) modules is also known as solar panels. Building Integrated Photovoltaic(BIPV) system consists of integrating photovoltaic modules into the building envelope, such as the roof or the façade.


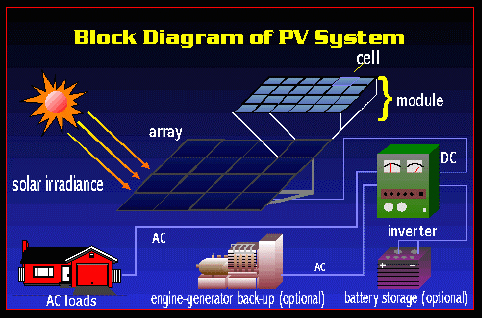
A complete BIPV system includes:
- The PV modules (which might be thinfilm or crystalline, transparent, semitransparent, or opaque);
- A charge controller, to regulate the power into and out of the battery storage bank ;
- A power storage system, generally comprised of the utility grid in utilityinteractive systems or, a number of batteries in stand-alone systems;
- Power conversion equipment including an inverter to convert the PV modules' DC output to AC compatible with the utility grid;
- Backup power supplies such as diesel generators and appropriate support and mounting hardware, wiring, and safety disconnects.
ARCHITECTURAL INTEGRATION
- ROOFING MATERIALS
- WALL COMPONENTS
- GLAZING
- SOLAR SHADING
- MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS


Building-Integrated Photovoltaic modules are available in several forms
1.Flat roofs
The most widely installed to date is a thin film solar cell integrated to a flexible polymer roofing membrane.
2.Pitched roofs
Modules shaped like multiple roof tiles.
It extends normal roof life by protecting insulation and membranes from ultraviolet rays and water degradation.

ThyssenKrupp Metal Fabrication,Germany
Plant screens are naturally well positioned to incorporate solar panels, receiving a large amount of solar radiation on at least two sides of the building.

Solar Louvers minimizes glare & over heating

3.Facade
Facades can be installed on existing buildings, giving old buildings a whole new look. These modules are mounted on the facade of the building, over the existing structure, which can increase the appeal of the building and its resale value.

Pitched roofing
& flat roofs
4.Glazing
(Semi)transparent modules can be used to replace a number of architectural elements commonly made with glass or similar materials, such as windows and skylights
THESE PV PANELS ARE MOUNTED ON A MOTORIZED PIVOTING VERTICAL AXIS AND TRACK THE SUN.
THIS NOT ONLY IMPROVES THEIR COLLECTION EFFICIENCY, BUT ALSO IMPROVES THEIR SHADING PERFORMANCE.
BILL CHALEFF, CHALEFF & ROGERS, ARCHITECTS


HERE THE PV PANELS REPLACE THE LOUVERS / MESH SOLAR SHADING DEVICE.
THIS IS AN EXCELLENT EXAMPLE OF WHAT ARCHITECTS AND ENGINEERS CALL AN “ELEGANT” DESIGN SOLUTION.
INSTEAD OF THE SOLAR SHADE “REJECTING” THE SUN’S ENERGY, IT INTERCEPTS IT AND CONVERTS IT TO A USEFUL PRODUCT.
GERMANY
Bringing Sunlight Inside


HOW IT WORKS:The key breakthrough is the miniaturized concentrator solar cell, which uses a lens with concentric grooves to focus collected light. Even though it is only the size of a postage stamp -- compared to the usual solar collector area that spans 4 x 4 feet -- the cell is much more efficient in collecting and reusing solar energy. The lens focuses incoming sunlight onto the solar cell. Microchannels at the base of the module transfer energy in the form of heat and light to wires contained inside. Each vertical stack of lenses rolls and tilts like a track blind, keeping the surface of the lenses faced to incoming sunlight as the sun changes position in the sky throughout the day. Incorporating these new cells into arrays could make solar energy an option that is competitive with other energy sources, reducing our dependency on fossil fuels.
35,000 km2 area of the Thar Desert has been set aside for solar power projects, sufficient to generate 700 GW to 2,100 GW.
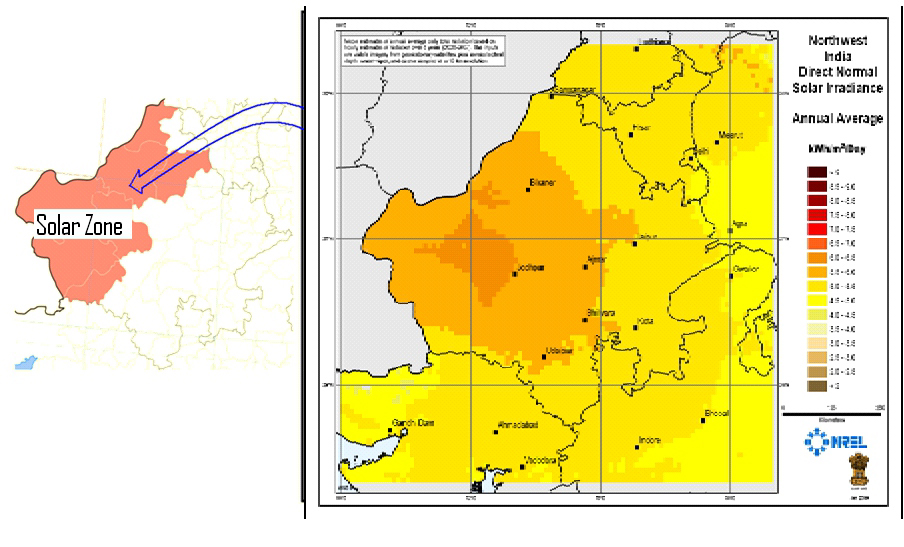
Rajasthan – Preferred State for Solar Energy
- The state in its western part blessed with abundant natural resource i.e. optimum sunshine and wind
- With more than 325 days of sunshine every year
- The state has the highest solar radiation in the country
- Jodhpur, popularly known as the SUN CITY of India
- Assured power evacuation arrangements in place. Setting up 400 / 220 / 132 KV network for solar and wind energy based power plants in progress.
- Sparsely populated. Revenue land is available in abundance
- Land is allocated at reserve price under G O R Policy Density of population – 165 per sq. km

Solar Power Projects- Current Status
- To support National Solar Mission,
- State approved 11 Solar Power Projects of 66 MW capacity.
- Land and Water allotment already done.
- Power Evacuation system approved.
- Projects migrated to NSM 2012
- In addition to this
- Two additional Solar Power Projects of 5 MW each are progressing under GBI scheme of MNRE.
Points to be considered
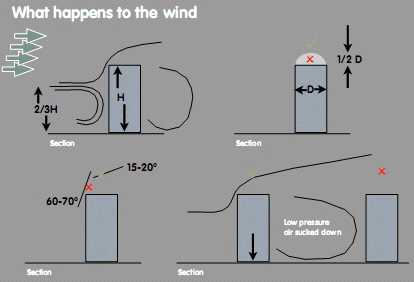
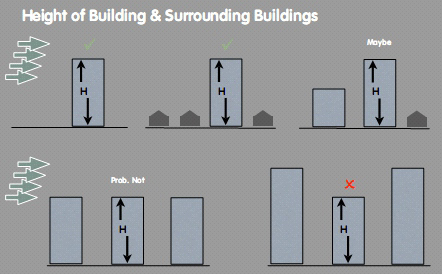
Points to be taken into consideration



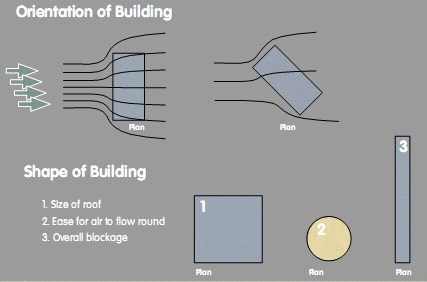
FACTORS
- Absolute Height of Building
- Height of Building above
- general heights of surrounding buildings
- Orientation of Building relative to more
- Dominant wind directions
- Shape of Building Absolute Size of Conurbation
- Location of Building Within Overall Conurbation
- Underlying Topography
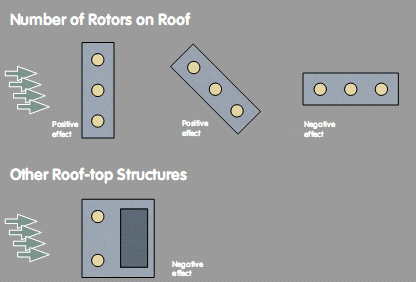
- Number of Rotors on Roof
- Depth of Building
- Other Roof-top Structures
Rotating Tower, Dubai
The world’s first moving building, a skyscraper with 80 independently rotating floors, is being planned for Dubai.
Wind Power:The power for the building will be supplied by horizontal wind turbines installed between the floors, thus avoiding the visual impact, one of the major drawbacks of the familiar “propellor” turbine. The blades are designed and constructed of materials to allow for quiet operation – a necessary feature, since they are only meters away from the residents. The architect, Dr. David Fisher, explained wind is a problem for most skyscrapers, and he decided to make use of it instead.


Solar Power:Photovoltaic solar panels will be installed on the roof of each rotating floor, and because they are constantly in motion, 20% of each roof will be open to the sky and to the sun.
Future Concept



The Tornado Tower is a spectacular modern and unique design that is characterized by a rotating facade, which generates power from high altitude winds. The exterior of the tower is outfitted with curved fins that harness the wind to generate clean energy to power the arts centre and the surrounding city as well. Pairing function and aesthetic, the roof of the tower boasts an undulating sea of pearls that meld into clouds, from which unparalleled views of the city are possible.
.png)




