Green Roof ……..a Need For Green India

Ar. Pawan Bhatt
M. Arch (Gold Medalist)
The phenomenon of rapid urbanization in India has resulted in urban sprawl and increased urban densities; this increase in urban density causes a reduction in urban open spaces, localized concentration of pollutants in the air and water,more and more energy consumption,more demand of recreational spaces, and increase in noise pollution due to vehicles. Urban sprawl also results in permanent loss of va luable agricultural land. To fill the requirement of green we need to explore green roof intoday's urban living.
"A green roof is a roof of a building that is partially or completely covered with vegetation and soil, or a growing medium, planted over a waterproofing membrane."
GREEN ROOF AND ITS EVOLUTION
Green roofs are not new;they have been considered standard construction practice in many countries for hundreds of yea rs. Green roofs can be traced back to the hanging ga rdens of Babylon and were known to exist in the Assy rian Empire.


TRADITIONAL AND MODERN GREEN ROOFS

Ziggurat-Mesopotamia

The Hanging Gardens of Babylon.
Le Corbusier envisioned urban areas with roads placed on roofs amid vegetation - 'his fifth point in A New Architecture was roof gardens' He also included a green roof in the design of Villa Savoye.
BENEFITS OF GREEN ROOF
Green Roofs are Energy Efficient
Green roofs reduce the heat flux through the roof,and less energy for cooling or heating can lead to significa nt cost saving.
In summer,the green roof protects the building from direct solar heat.In winter,
conserves heat gained from sola r radiat ion which in turn gets reradiated in the internal space at night after a time lag. In winter; the green roof minimizes heat loss through
added insulation on the roof. Energy conservation translates into fewer greenhouse gas emissions.

Villa Savoy.
Green roofs reduce storm-water runoff
During heavy or continuous rain, runoff can overwhelm storm-water infrast ructure and potentially damage waterways and fish habitat. Green roof as a growing media retains rainwater,together w ith plants, return a portion of this water to the atmosphere through evaporation and transpiration. Storm water that does leave the roof is delayed and reduced in volume. Storm water that runs off a green roof is cleaner tha n runoff from a conventional roof. Retention and delay of runoff eases stress on storm water infrastructure and sewers.
Ecological Advantages
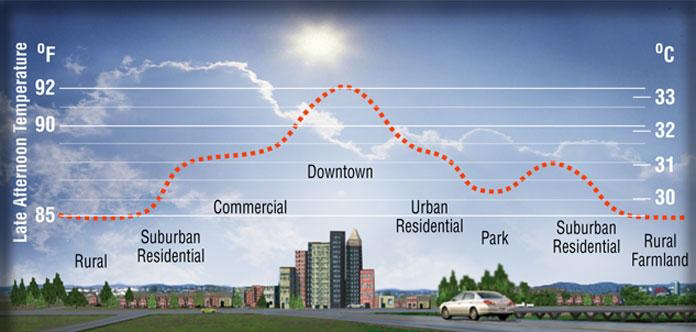
Plant leaf traps dust particles from the ambient air,and evapotranspiration cools ambient temperatures,so both ways the air quality improves towa rds comfortable one.This results in less smog and less ground leve l ozone,thus leading to less heat
trapping.Temperat ures in the urban core can be 30-50 C warmer than rural and suburba n areas this leads to Reduced Urban Heat Island profile.
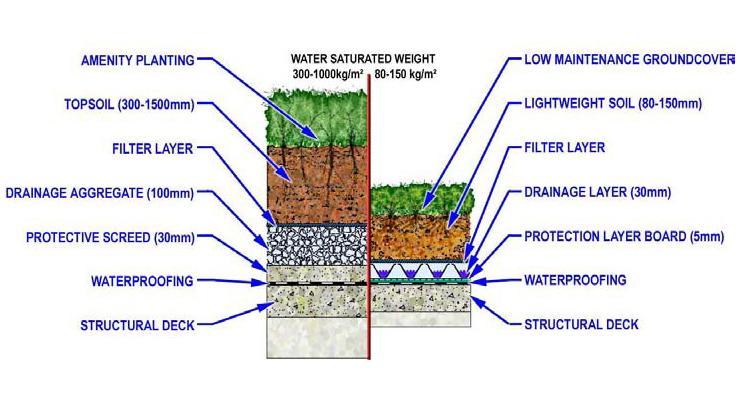
COMPO NENTS OF GREEN ROOF
Green roof can be of differe nt types depending on their construction technical details. In general this has been classified in three different types.
Extensive Green Roofs
Extensive green roofs are defined as usually being developed for aesthetic and ecological reasons. These usually have thin growing mediums {4-8") and lightweight; low-maintenance plants are used for extensive green roofs
Intensive Green Roofs
Intensive green roofs are typically having thick growing medium
{8-12 inches,or more) and typical ga rden va rieties of plants are used.
.jpg)
FORD HEAD OFFICE IN U.S.A.
(Source and copyright © Earth Pledge, 2005)
Conventional (Intensive) and Lightweight (Extensive) Green Roof Systems
(Source and copyright © Urbis Ltd., 2006)

FORD HEAD OFFICE IN U.S.A.
| Component | Function | Materials used |
| Waterproofing | Prevents water from entering the buildings and allows water runoff during rainy periods | Modified bitumen reinforced with fibre glass or non-woven polyester |
| Root Repellent | Prevents plants from damaging the waterproof membrane in the long term | Copper linings |
| Drainage | Maintains proper drainage to the overlying growth media and ensures that plants do not drown from exposure to excess water and that water vapor can be released | Porous mats, granular media or polystyrene |
| Filter Cloth | Ensures that fine sediments from the substrate do not clog the drainage layer and helps prevent roots from reaching the repellent system | Non-woven!' non -biodegradable Polyester or polyropylenepolyethylene mats |
| Growing medium | Used as fire resistance, insulation and waterproofing protection and as the growing media for vegetation | Mixtures or inorganic (vermiculite, clay, volcanic rock and coarse sands) and organics |
| Vegetation | Insulates the system, protects biodiversity, air particle filter, aids in storm water management, CO 2 sequester and 0 2 producer and serves as a transpiration media | Perennial, biennials or annuals |
Source: DeNardo et al., 2003; Peck et al., 1999.
Podium Gardens
Podium Gardens are usually 2 to 10 storeys up forming the base of a residential or office towe r.These gardens are usually intended for full access by the buildingoccupants or the public and are therefore always Intensive Green roofs.


SUPER NOVA, NOIDA

PRECAUTIONS FOR NEW GREEN ROOF
a)Water proofing is a most layer therefore care is to be taken while applying layer. In an old building where retrofitt ing should be conducted three should be continuous separat ion between the membrane and the plant laye r,since the membrane w ill be susceptible to root penetration and micro-organic activity.
b)If the drainage layer is too thin or if the routes to the roof drains become blocked, leakage of the membrane may occur, due to continuous contact with water or wet medium. There fore dra inage laye r is to made as per design of roof if its is intensive then drainage layer should not be less than 20 mm w here as for intensive roof drainage layer should vary between 45 mm to 60 mm
c)Green roof retains much of the rain that falls on it, maintaining proper drainage on the roof is still very importa nt aspect. Parapets, edges, flashing, and roof penetrations made by skylights, mechanical systems, vents,and chimneys must be well protected with a gravelskirt.
d)For intensive green roof root penetration membrane is mandatory
Plants
Location,wind rainfall, air pollution, building height,shade, and soil depth are all factors in determining what plants can be grown and where. The ability of plants to survive on a green roof is directly proportional to the amount of maintenance time an budget allocated to the project,particularly in the first two years when they are getting estabIished.
Maintenance
Both plant maintenance and maintenance of the waterproofing membrane are required for the Green Roof
Depending on whether the green roof is extensive or intensive,required plant maintenance will range from two to three yearly inspections to check for weeds or damage,to weekly visits for irrigation,pruning,and replanting.
Capital Costs
Capital Costs are largely dependent on labor, materials and access difficulties. However,compared with entire building costs in India, green roofs costs both intensive and retrofitted extensive are very small. A range of Rs. 600/ m2 to 1500/ m2 (average 1200/ m2) is estimated for Local Extensive Green Roof in new construction.
.png)